6 January 2026
How to build an AI chatbot from scratch: startups edition
Chatbots grew up. Learn how to turn scripts into conversations that sell with LLMs
Solutions
Chatbots have evolved. The pop-ups and scripted assistants are no longer enough. Today, LLM chatbots — powered by Large Language Models — can hold real conversations, provide actionable insights, and integrate deeply with business systems.
But the real challenge isn’t deciding whether to use AI. It’s learning how to build an AI chatbot that’s reliable, secure, and genuinely useful for your users.
For startups, the opportunity is massive: faster onboarding, smarter support, and personalized user experiences without hiring a full team. But the difference between a quick demo and a production-grade LLM chatbot project comes down to data, architecture, and iteration.
This guide walks through what every startup should know before building a custom LLM-powered chatbot — or as we like to call it, turning scripts into real conversations that sell.
Table of contents
What an LLM chatbot really is
TL;DR:
Chatbots have evolved from rule-based scripts to intelligent assistants powered by large language models (LLMs). Early bots followed rigid flows or matched keywords, while modern LLM chatbots — like those built on GPT, Claude, or Llama — can understand context, reason, and generate natural, human-like responses. They don’t just retrieve data but interpret and explain it in real time.
An AI chatbot is software that uses artificial intelligence to communicate with users through natural language — text or voice — to help them find information, complete tasks, or get support. (If you want a deeper breakdown of what it takes to build the best AI chatbot for business, we wrote more about this in our hands-on guide.)
Depending on how you build your own AI chatbot, it might follow simple rules or use advanced LLM models for chatbots to reason, learn, and adapt dynamically.
At its core, an LLM chatbot is a conversational interface — a digital assistant that interprets user input and generates responses naturally. You can build a chatbot AI ranging from simple rule-based systems to complex setups that handle reasoning, data retrieval, and task automation.
If you plan to build an AI chatbot for your website, it’s worth understanding the technical layers that make it work: natural language understanding (NLU), information retrieval, and software integration. These elements determine how “intelligent” your bot actually feels.
Types of AI chatbots
Chatbot type |
What it does and when to use it |
|---|---|
|
Rule-based chatbots |
These are the simplest kind; think of them as interactive flowcharts. They follow if-this-then-that rules and respond only to predefined options. If you’ve ever clicked through a support bot that made you pick between “Order status” or “Refund,” that’s a rule-based one. Reliable, yes. Flexible, not so much. It’s where most people start when learning how to build an AI chatbot from scratch. |
|
NLP chatbots |
Then came natural language processing (NLP). Instead of just matching keywords, these bots can identify intents — what the user is trying to do — and extract key entities like names, dates, or order numbers. If you plan to build a chatbot AI system that handles clear, repetitive tasks like booking or tracking, NLP chatbots are your go-to. But they still require training on every possible intent. |
|
Retrieval-based chatbots |
A step closer to intelligence: these bots don’t generate answers but find them. They search through knowledge bases or FAQs using semantic search to locate relevant text. It’s a great setup if you want to build an AI chatbot with a custom knowledge base — perfect for internal knowledge assistants or customer support teams with a large set of pre-written answers. |
|
LLM-based chatbots |
Now we’re in generative territory. LLM chatbots don’t just look up answers; they create them on the fly. Built on LLM models for chatbots like GPT, Claude, or Llama, they understand nuance, phrasing, and tone. You can build your own AI chatbot or even create your own LLM chatbot using your company’s data for highly personalized, context-aware responses. Imagine a customer asking about a complex refund policy. Instead of searching for keywords, the LLM chatbot reads the policy, interprets the question, and explains it naturally, just like a human would, with no pre-programmed answers required. |
|
Hybrid chatbots |
Most real-world chatbot projects use a mix of methods. A hybrid LLM chatbot might rely on an LLM for natural conversation but still use NLP or rule-based logic for structured actions — like confirming a payment or checking inventory. It’s a balanced approach if you want to build an AI chatbot that blends creativity with predictable, reliable workflows. |
|
Agentic chatbots (the next frontier) |
The newest wave builds on LLMs but adds reasoning, memory, and tool use. These “agentic” chatbots don’t just answer questions — they do things. They can plan tasks, pull live data, trigger workflows, and adapt based on feedback. Think of them as mini AI teammates that can learn from each interaction. |
Why LLM chatbots stand out
Each generation of chatbots has solved a different problem — from automating FAQs to understanding intent. But the real leap came with LLMs. Suddenly, a chatbot could do more than just reply: it could reason, rephrase, summarize, and adapt its tone to the user.
That shift is why startups are betting big on LLM chatbot projects. They’re not just cheaper helpdesk tools anymore — they’re becoming the new interface between users and digital products.
What’s the difference between LLM and a chatbot
A chatbot is the interface — the thing users actually talk to. It’s the system that interprets questions, keeps track of the conversation, and sends back responses. But what powers those responses depends on the underlying technology.
An LLM (large language model) is the brain behind the smartest chatbots. It’s the model trained on massive amounts of text data that enables the chatbot to understand context, reason, and generate natural responses.
In other words:
- The chatbot is the shell: the communication layer that manages interaction.
- The LLM is the engine: it drives understanding, reasoning, and generation.
When you build an AI chatbot, you can choose to power it with an LLM for natural, dynamic conversations or stick with simpler NLP logic for more predictable tasks. So, if you’re still wondering if ChatGPT is a chatbot or an LLM, it’s both: ChatGPT is an LLM that powers a chatbot interface.
This distinction matters when deciding how to build AI chatbots for your product. You can design a custom chatbot that connects to an LLM, or build a full LLM chatbot project that integrates reasoning, memory, and live data to go far beyond scripted dialogue.
Start your chatbot project with experts who ship
Share your idea and get a clear, realistic path from prototype to scalable AI product.
How LLM chatbots actually work (in plain English)
At a high level, an LLM chatbot is like a conversation engine: it reads what users type, interprets the intent, and produces a response that fits the context. But under the hood, several layers work together to make that interaction reliable. Let’s break it down without the jargon.
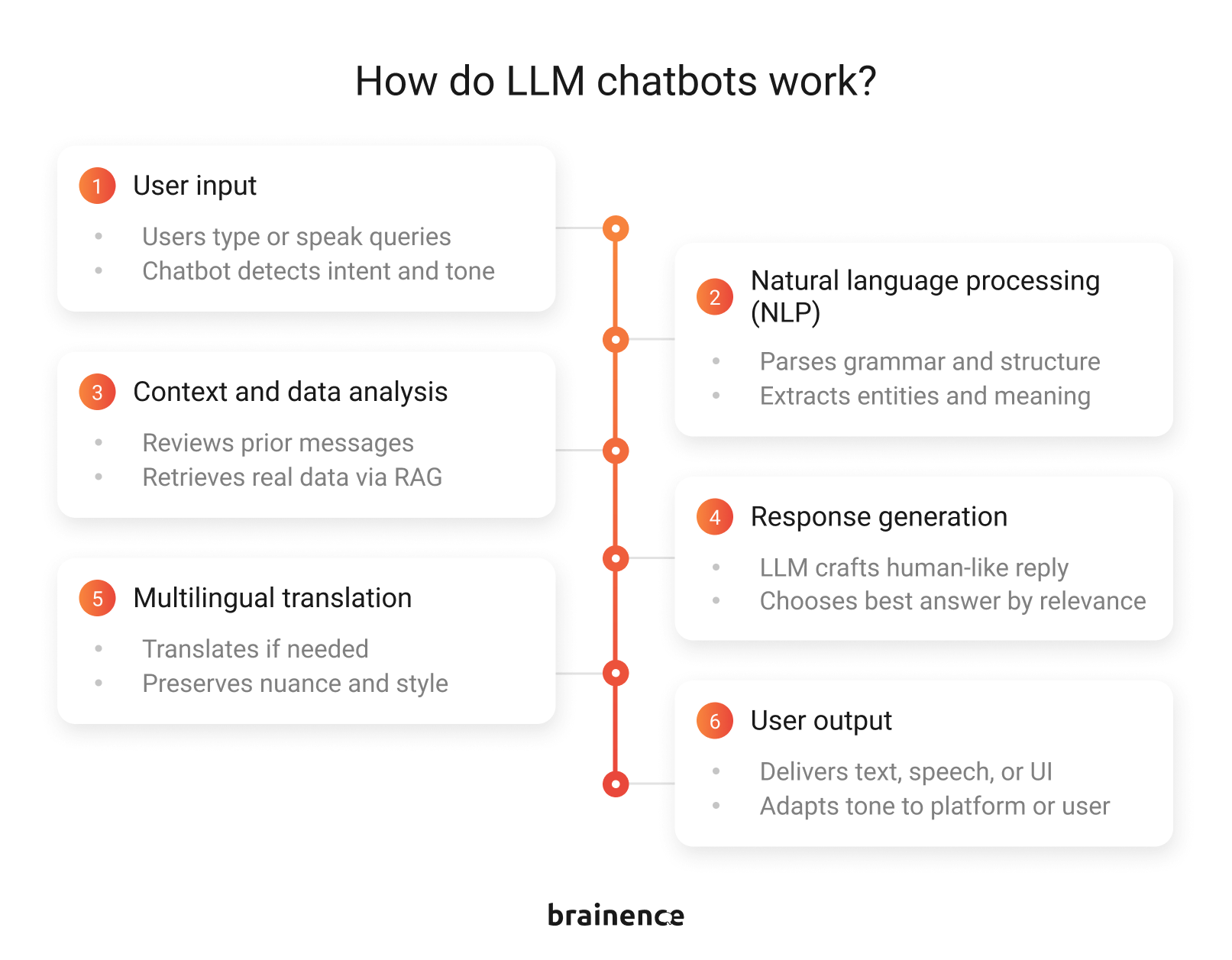
1. User input
Users interact via text, voice, or structured queries. The chatbot picks up context clues like urgency, sentiment, or user role to understand what’s really being asked. This is the raw material the AI will work with.
2. Natural language processing (NLP)
The input is analyzed to detect intent, extract entities like names, dates, or product IDs, and parse grammar and sentence structure. Tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and semantic analysis turn raw language into structured data that the AI can work with.
3. Context and data analysis
The bot reviews prior messages to keep multi-turn conversations coherent. It can also query external sources like knowledge bases, product catalogs, or CRMs using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), grounding answers in real data and reducing hallucinations.
4. Response generation
Here’s where LLM models for chatbots like GPT or Claude shine. The model crafts a human-like reply by blending its training knowledge with retrieved information. Each response is scored for clarity, tone, and relevance before being sent to the user.
5. Multilingual translation
If needed, the response is translated into the user’s language, preserving meaning, nuance, and style. This ensures consistent, high-quality communication for global users.
6. User output
Finally, the chatbot delivers its response—via text, speech, or interactive elements like buttons. When you build your own AI chatbot, you can fine-tune this step to match your platform’s style and audience. That’s what makes every interaction feel seamless and human-like.
The benefits of LLM-based chatbots
A chatbot that talks back isn’t automatically valuable. Usefulness comes from what it does, not how clever it sounds. The best LLM chatbots turn conversations into actions and insights. Here’s what separates a genuinely useful chatbot from a fancy gimmick:
It solves real problems
Your users aren’t impressed by chatter; they want results. A helpful chatbot guides them through onboarding, answers questions clearly, or completes tasks like checking orders or scheduling meetings. Every interaction should have a purpose.
It integrates with your systems
A chatbot that can’t access your data is just talking. LLMs shine when connected to CRMs, product databases, knowledge bases, or internal APIs. That’s how they provide precise, contextual answers instead of generic responses.
It adapts to the user
A single chatbot tone doesn’t fit every scenario. Useful chatbots adjust language, detail, and approach depending on the user’s familiarity, urgency, or role. They can be friendly, professional, or concise — whatever the situation demands.
It handles complexity gracefully
Users often have multi-step requests. A useful chatbot can maintain context across turns, manage follow-up questions, and escalate when human intervention is needed — without breaking the conversation.
It learns and improves
Feedback loops matter. Logging interactions, tracking errors, and updating the model or prompts over time ensures the chatbot stays accurate, relevant, and aligned with your business goals.
How to build a custom AI chatbot using your own data
The difference between a prototype and a production-ready assistant comes down to planning, architecture, and iteration. Continue reading for a practical, step-by-step roadmap for startups building AI chatbots.
1. Define the problem and success metrics
Start with clarity. What real problem will the assistant solve: reducing support load, improving lead conversion, or speeding up onboarding?
Define measurable outcomes (e.g., ticket volume ↓30%, NPS ↑10 points). These goals shape your model selection, data design, and user experience.
2. Choose the right model
Not every large language model fits every workload.
- Cloud-based APIs like GPT or Claude are fast to deploy and scale, but lock you into provider pricing and data policies.
- Open-source models like Llama, Mistral, or Phi-3 let you self-host for more control and privacy but require MLOps setup and tuning (LoRA or QLoRA adapters, quantization).
Decide based on your data sensitivity, performance needs, and long-term cost strategy.
3. Design your data strategy
A chatbot is only as useful as the knowledge it can access. Map your internal data sources — product documentation, FAQs, support logs, or CRMs — and structure them for retrieval. Implement Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines using frameworks such as LangChain or LlamaIndex.
Key steps:
- Clean and chunk data.
- Embed it into vector databases (e.g., Pinecone, Qdrant, or Weaviate).
- Retrieve the most relevant context at runtime.
4. Build and test an MVP
Start lean:
- Create a narrow-scope prototype and validate it with early users.
- Track accuracy, latency, and satisfaction.
- Use logs to identify recurring prompt failures or missing data.
- Focus on user feedback before scaling infrastructure — every iteration improves ROI and reliability.
5. Integrate with your systems
Connect the chatbot to the CRMs, ERPs, or support platforms via secure APIs. Add automation triggers — booking, data entry, report generation — so the bot can execute tasks, not just answer questions. This step defines the transition from chatbot to agentic AI.
6. Implement monitoring and governance
After launch, treat your assistant like any production system.
Set up observability for:
- Latency, error rates, and API usage.
- Data drift and model output quality.
- Privacy compliance (GDPR, SOC2, etc.).
Use dashboards (Prometheus, Grafana, or OpenTelemetry) and prompt versioning to track performance and rollback if needed.
7. Iterate and scale
Once the MVP works reliably, expand use cases and data access. Optimize prompts, fine-tune domain-specific adapters, and experiment with smaller models for cost efficiency. Introduce caching layers or hybrid retrieval to handle traffic spikes.
A scalable LLM chatbot is part AI, part software engineering, and part user experience design. Skipping any of these layers risks building something that talks a lot but does little. Partnering with an experienced development team like Brainence ensures all three elements come together smoothly, turning AI potential into a real business advantage.
Start your chatbot project with experts who ship
Share your idea and get a clear, realistic path from prototype to scalable AI product.

Challenges of building your own AI chatbot
Behind the demos and headlines lie hidden challenges that can trip up even experienced teams. Knowing them upfront separates projects that succeed from ones that stall.
Hallucinations are real
LLMs sometimes generate answers that sound plausible but are factually wrong. Without safeguards, a chatbot could mislead users, damage trust, or create compliance risks. Effective systems combine retrieval from reliable data sources, prompt engineering, and fallback logic to keep the AI honest.
Context management is tricky
Maintaining multi-turn conversations is more complex than it seems. Chatbots must track user intent, remember relevant details, and know when to forget outdated info. Poor context management leads to repetitive or nonsensical answers.
Data privacy and security matter
Your chatbot might access sensitive internal data — customer info, product roadmaps, or financials. That demands secure storage, controlled access, and careful integration. Not every AI API handles privacy the way enterprise systems require.
Costs can spiral
LLM APIs aren’t free, and computation-heavy models can become expensive at scale. Startups often underestimate usage patterns, leading to surprise bills. Monitoring, caching frequent queries, and optimizing prompts help control costs.
Integration complexity
Connecting the AI to multiple systems — CRMs, ERPs, knowledge bases — is where projects often get stuck. It requires engineering discipline, reliable APIs, and thoughtful orchestration to make the chatbot not just smart, but actionable.
User expectations
A shiny chatbot sets expectations. If it can’t deliver consistently, users get frustrated quickly. Clear onboarding, proactive fallback strategies, and transparent scope help manage perception.
Create your own LLM chatbot
If you want an AI chatbot that goes beyond a clever demo, the first differentiator is your data. And the second one is the team that knows how to turn that data into a reliable product.
At Brainence, we’ve spent nine years building production-grade software for fast-growing startups and global enterprises. From healthcare and e-commerce to real estate, logistics, fintech, and data-heavy systems, our teams know how to architect platforms that handle real workloads, integrate with messy legacy systems, and still feel effortless for end users.
That experience translates directly into building LLM-powered chatbots that actually deliver:
- Deep integration, not surface-level chat. We connect your chatbot to CRMs, ERPs, product databases, internal APIs, and custom workflows so it becomes part of your core product.
- RAG the right way. Clean data, smart chunking, vector storage, hybrid search, and domain grounding. We don’t “just plug in LangChain”; we architect retrieval that scales.
- Agentic capabilities where they make sense. Not every chatbot needs to be an agent. But if yours does (planning tasks, pulling live data, triggering workflows), we build it without breaking security or performance.
- Enterprise-grade privacy and security. Whether you need SOC2 compliance, GDPR alignment, isolated deployments, or full control via self-hosted open-source models, we design for the level of privacy your business requires.
- Performance that doesn’t destroy your budget. Model selection, caching, prompt optimization, inference tuning, and cost modeling — we help you avoid the “why is our AI bill $20k this month?” moment.
- A team that actually ships. Full-stack engineers, AI/ML specialists, QA, PMs, and DevOps who build platforms, not prototypes.
Most importantly, we make sure your chatbot becomes a business asset: reducing support load, increasing conversion, simplifying onboarding, and powering a better product experience end-to-end.
If you’re thinking about building an LLM-powered chatbot (or upgrading the one you already hacked together), let’s talk. Send us your project details and get a realistic plan and a quote for your custom AI chatbot.
Questions you may have
Can I build an AI chatbot for my website that uses a custom knowledge base?
Yes. You can build an AI chatbot for your website using a custom knowledge base by implementing an RAG pipeline that connects your bot to FAQs, documentation, product catalogs, or internal systems. This allows the chatbot to answer accurately using your real data, not generic training info. Many startups now build AI chatbots with custom knowledge bases to reduce support load and improve onboarding without expanding their teams.
What challenges should I expect when starting an LLM chatbot project?
LLM chatbot projects often run into the same challenges: hallucinations, complex context management, securing sensitive data, integrating with CRMs or ERPs, and controlling API costs. Startups frequently underestimate how much engineering sits behind a “simple” chatbot — from model selection to observability, caching, prompt tuning, and governance. Solving these challenges is what separates a demo from a production-grade AI chatbot that users actually trust.
How do I decide which LLM models for chatbots to use in my project?
Choosing an LLM model is like choosing your engine. It defines speed, cost, and how far you can scale.
Cloud options like GPT or Claude are fast and high-quality, but pricey and less flexible. Open-source models like Llama, Mistral, or Phi-3 give you privacy and cost control, but require proper MLOps.
Focus on a few core criteria:
- Data sensitivity: If you handle internal or confidential data, consider self-hosted.
- Latency: Real-time apps need lighter, faster models.
- Budget: Heavy API usage adds up quickly.
- Scaling: More users = more reason to optimize early.
- Customization: Domain tuning or agentic behavior often requires open-source.
- Compliance: Strict industries need stricter control.
How do LLM chatbots work under the hood, and what makes them reliable?
LLM chatbots work through several layers: NLP for understanding user intent, retrieval pipelines for accessing your data, LLM-based generation for answering, and context tracking for multi-turn conversations. Reliability comes from grounding the model in your knowledge base, using hybrid search, adding guardrails and fallback logic, and monitoring accuracy over time. A reliable LLM chatbot example always combines AI models with real engineering discipline.
Contact us

The most impressive for me was the ability of the team to provide first-class development and meet all the deadlines.

The team proactively comes up with solutions and is eager to deliver high-quality development support.

I was blown away by the knowledge that Brainence has about web app development, UX and optimisation.